Introduction
Balance Sheet Certification (BSC) is the certification of the closing balances of all the company accounts that form part of the company's balance sheet to ensure that the entries passed to derive the closing balances are recorded and appropriately classified so that entries in the balance sheet are appropriate.
Balance Sheet Certification is an essential step in financial reporting, and it often requires hundreds of person-hours across the record-to-report (R2R) function. Companies typically deploy tools such as Excel, emails, shared drives and workflow to help, but more is needed to solve the underlying issues. Some may use point solutions designed to help complete the certification and certification process. Still, these are often designed to address the effectiveness of the balance sheet certification process, with only slight improvements in automation and minimum efficiency gains. Evidence shows that both methods still leave a substantial amount of work that must be performed manually.
Redwood's approach to the automation of Balance Sheet Certification delivers the flexibility needed and the financial intelligence to provide higher levels of automation than point solution applications on the market today. Between 60% and 70% of certification work is performed by the preparers, and the key to removing the manual burden is auto-certification of almost everything a preparer must do. Simply analyzing the account based on balances can mislead and can inaccurately portray the activity that occurred in the account for the period being reconciled. Therefore, it is equally important to analyze and certify the underlying transactions and the balances themselves. Redwood helps customers apply auto-certification rules at the balance level first, then automatically check the line items to ensure the account can be auto-certified based on the balance.
Balance Sheet Reconciliation (BSC) Components
Balance Sheet Reconciliation contains three components:
-
Account Reconciliation Workbench: Overview of all certification processes of a period with the ability to drill down into accounts
Note: Note SAP and Redwood use a note system to communicate important pieces of information to their customers.
You can access SAP Notes at https://launchpad.support.sap.com and Redwood Notes at https://notes.redwood.com/<Number>.: This was formally known as Balance Sheet Certification Dashboard
SAP and Redwood use a note system to communicate important pieces of information to their customers.
You can access SAP Notes at https://launchpad.support.sap.com and Redwood Notes at https://notes.redwood.com/<Number>.: This was formally known as Balance Sheet Certification Dashboard The dashboard allows you to monitor one or more systems using graphs and dials..
The dashboard allows you to monitor one or more systems using graphs and dials.. -
Certification page: Prepare and approve the certification
-
Chain template and process definitions: Chain template to build from
Standard BSC Functionality
Preconfigured certification routines validate the balances with underlying applications, such as ERP![]() Enterprise resource planning (ERP) refers to a type of software that organizations use to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk management and compliance, and supply chain operations. A complete ERP suite also includes enterprise performance management, software that helps plan, budget, predict, and report on an organization’s financial results., bank statements, files or other source systems. Redwood’s automated routines then compare account balances between these sources and identify and report any discrepancies so accounting staff can investigate them. Some of the features of Redwood’s Balance Sheet Certification include:
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) refers to a type of software that organizations use to manage day-to-day business activities such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk management and compliance, and supply chain operations. A complete ERP suite also includes enterprise performance management, software that helps plan, budget, predict, and report on an organization’s financial results., bank statements, files or other source systems. Redwood’s automated routines then compare account balances between these sources and identify and report any discrepancies so accounting staff can investigate them. Some of the features of Redwood’s Balance Sheet Certification include:
-
Certification templates and checklists: Contains predefined templates for single-sided and two-sided certifications that contain header data, line item table, and the breakup table.
-
Integrated storage of supporting documentation: Allows users to add comments and supporting files for certification within the application.
-
Automated review and approval workflows: Easily assign reviewers and configure approval workflows for line-item changes.
-
Definition of monitoring of corrective actions reference: Generate incoming and outgoing actions that are then completed by other users.
-
Posting related corrections and journals directly into ERP: Sync line item changes from the BSC portal to the backend ERP system.
Redwood's catalog of pre-automated financial tasks standardizes and automates any type of certification and cuts out costly, tedious processes. The result is that Redwood’s solution can automate up to 95% of Balance Sheet Certification tasks. Balance sheet integrity via our automation releases financial and accounting teams to focus on value-added activities. In addition, it helps organizations achieve a key milestone on the journey to digital finance by providing transparency into accounting performance and operations and moving beyond manual, error-prone processes.
BSC Process Overview
The Balance Sheet Certification in Redwood's solution follows some basic steps explained in this section. Some of these steps happen in a fully automated way, and finance users only need to interact with the certification process at certain stages of the process. The Balance Sheet Certification in Redwood is a preconfigured process, which can be customized according to your organization's needs. For more information on how to change the configuration, please refer to the technical guide.
The following are the high-level milestones in the certification process:
- Retrieve all information: In this stage, the process retrieves all relevant information for the certification , such as balance-level information and line item-level information for the account(s) being certified.
- Apply certification rules: Based on the defined rulesets, the certification will perform the checks to auto-certify the account and individual line items.
- Workflow to preparer: After the automatic rules have been applied, the resulting information is filled into the certification Form and presented to the responsible preparer. The preparer receives a link to the form so that they can access the data and finish the preparation tasks that are required for this certification. The preparer can also restart the certification to retrieve more updated information (start over again from step 1).
- Workflow to approver: After the preparer has completed their task, the certification is routed to the responsible approver. The approver receives a link to the form, so that they can access the data and review the certification. If the approver accepts the certification, it proceeds to the final step. If the approver rejects the certification it is routed back to the preparer.
- Finalize certification: The certification is locked so that the information becomes read-only.
Two-sided Reconciliation
In some cases, there is a need to reconcile different data sources, e.g., Bank Reconciliation, Bank Account in ERP versus Bank Statements. The two-sided reconciliation as part of the Balance Sheet Certification extends the existing balance sheet product. Two-Sided Reconciliation allows you to create matches between two data sources. You select the rows that must be matched from the left/right data sources and input a matching ID![]() The unique identifier of an item.. The selected rows are removed from the input source tables and placed into the work area table.
The unique identifier of an item.. The selected rows are removed from the input source tables and placed into the work area table.
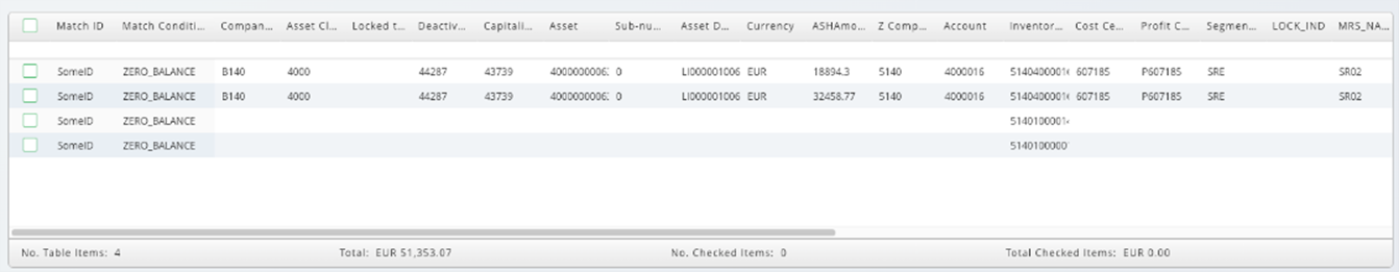
Once you create all the required matches between the data sources, the following outputs are added to the job:
- The unmatched left rows are written to
left_unmatched_rows.rtx - The unmatched right rows are written to
right_unmatched_rows.rtx - The matched rows, including the user-generated match ID field, are written to
matched_rows.rtx
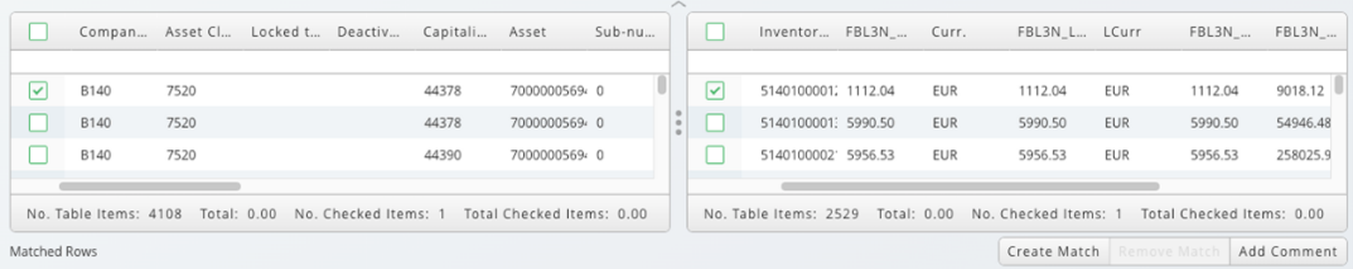
Follow these steps to create a match:
- Select rows from the source tables and create a match between them to populate a Match ID and Match Condition. These fields are added to each line-item which is placed into the match table.
- To create a match between rows, select the check-box on a row from the left or right input sources and click Create Match. A dialog appears containing inputs for the Match ID field and a drop-down list to select a match condition.
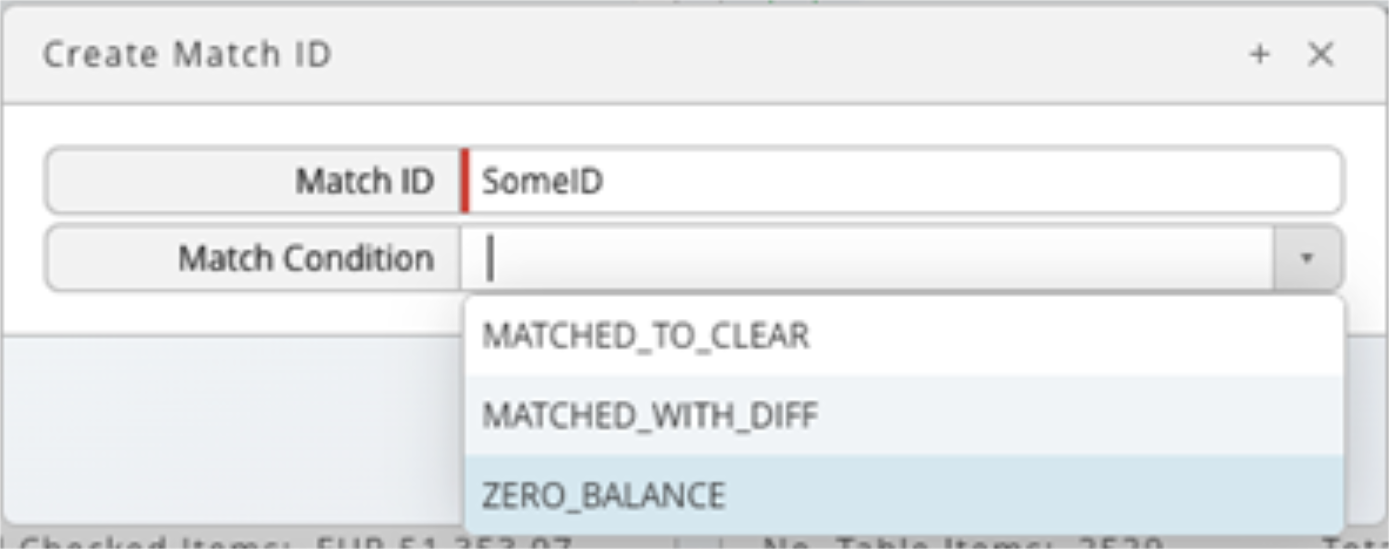
When the required fields populate, the matched rows move to the work area table. The Match ID and Match Condition columns contain the inputted values.